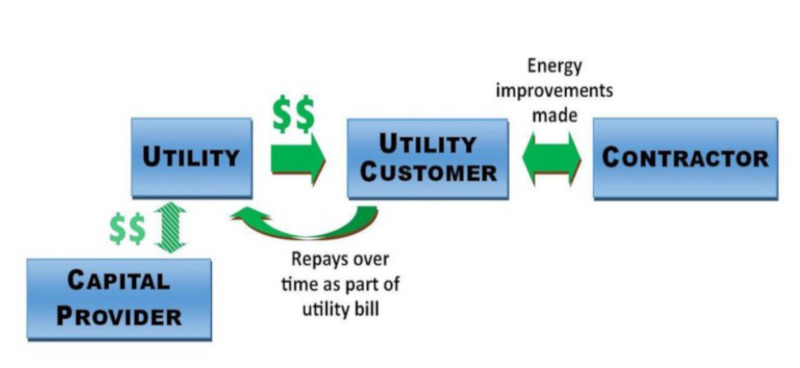
On-bill financing
On-bill financing and on-bill repayment programs provide two options for property owners to pay for investments in clean energy upgrades through their utility. While electric utilities and natural gas companies typically run on-bill programs, there is an opportunity for state and local governments to capitalize on new on-bill loan funds and/or provide credit enhancement47for existing on-bill funds. Depending on the programs available in a given jurisdiction, some government entities may also be able to take advantage of on-bill programs to finance projects for their own facilities.
On-bill financingallows the utility to incur the cost of the clean energy upgrade, which is then repaid on the utility bill. On-bill repaymentoptions require the customer to repay the investment through a charge on their monthly utility bill as well, but with this option, the upfront capital is provided by a third party, not the utility. Additionally, on-bill repayment allows for a streamlined process as utilities already have a billing relationship with their customers, as well as access to information about their energy usage patterns and payment history. In some on-bill repayment programs, the loan is transferable to the next owner of the home or building.33
Advantages and disadvantages of on-bill financing
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
As the successful example of on-bill financing the implementation of the UK Green Deal is often cited when loan facility that can last for 25 years and can be repaid on via a charge on an energy bill. It is a standardization of measures and loan contracts, which several UK local authorities set up in collaboration with private delivery partners.34