Current EE financing situation in partners areas
2.2.1 EE services
- Following table provides basic comparison of EE services provided by particular partners in each are.
Name of the region / area |
Scale of services provided |
Amount of funds needed annually (if not specified) |
Sources of financing |
Emilia – Romagna |
Inventory of Regional Thermal Plants - CRITER |
3.000.000 EUR |
100% own sources (Regional budget) |
|
Regional Energy Building Certification System- SACE |
3.000.000 EUR |
100% own sources (Regional budget) |
|
Zlínský kraj |
Support citizens / public authorities / companies in the acquisition of EE funds (dissemination and promotion of co-financing programs and other financial resources) |
10.000 EUR |
Regional budget EU projects |
|
Initiation and coordination of bulk energy purchase (natural gas and electricity) for organization established by the Zlín Region and towns and villages of the Zlín Region |
25.000 EUR |
Regional budget EU projects |
|
|
Technical advisory in energetics provided to citizens of the Zlín Region related to EE and refurbishment of buildings and RES utilization. |
10.000 EUR |
Regional budget |
|
|
Energy management provided to organisations and towns of the Zlín Region |
50.000 EUR |
Regional budget |
|
|
Initiation and preparation of EE and RES projects submitted to various OP |
70.000 EUR |
Regional budget EU projects |
|
|
International cooperation in the field of energy planning, RES and EE promotion within the the cooperation with other EU regions |
40.000 EUR |
Regional budget EU projects |
|
Tolna Megye |
Ca. 4000 EUR per training |
EU projects and national OPs |
|
|
Monitoring of implementation of energy efficiency policy - update the county’s development plans as a general role. |
Covered by County budget |
100% own sources |
|
|
Support citizens / public authorities / companies in the acquisition of EE funds (dissemination and promotion of co-financing programs and other financial resources) |
One project can apply for max 16.130 EUR. |
Environment and Energy Efficiency OP 3.225.806 EUR budget on national level |
|
|
Planning and policy (SEAP, SECAP, yearly investment plans, general/city development strategy etc. |
Ca. 9.600 EUR in average per settlement. |
Financed by the municipalities. |
|
Velenje |
Energy management (for running of local energy agency-KSSENA)energy |
50.000 EUR |
Municipal budget |
Koprivnica |
Energy services provided by REA North - Project development, project and investment management, technical advices |
60.000 EUR |
100% own sources (municipal budget) |
|
In-house energy expertize, energy related administration, energy investments, EU projects etc. |
50.000 EUR |
100% own sources (municipal budget) |
|
|
Capacity building and promotion to employees, private sector and citizens regarding EE, energy planning , RES etc. |
10.000 EUR |
Own sources (municipal budget) + external sources |
|
Płońsk |
Planning and policy – City Development Strategy including ecological policy, which set up targets related to EE – e.g. increasing usage of RES, boosting EE public and housing sector |
1.300.000 EUR for future investments related to EE |
Own sources (municipal budget), EU funds |
|
Planning and policy – City Revitalization Program - Framework for investment realization |
2.000.000 EUR for future investments related to EE |
Own sources (municipal budget), EU funds |
|
|
Educational activities - lectures in schools and special events |
5.000 EUR |
Own sources (municipal budget) |
|
|
Partnership within Płońsk Energy Cluster to to promote and initiate local projects in the field of energy production, implement energy-saving and highly-efficient technologies etc |
n/a |
Own sources (municipal budget) |
|
Lubawka |
This partner is primarily focused on EE projects – see the section EE projects below this table |
n/a |
n/a |
Judenburg |
Financial support for EE - Subsidies for thermal insulation, installation of biomass heating systems, thermal solar energy and PV-systems for households and businesses |
15,000 EUR |
Core financing |
|
Development and maintaining of energy management |
5,000 EUR |
Core financing |
|
|
Energy efficiency advice
|
20,000 EUR |
Core financing |
|
|
Planning, implementation and monitoring of EE-policies (SEAP, eea-annual plans) |
15,000 EUR |
Core financing |
|
|
Planning and monitoring of EE investments in public buildings |
15,000 EUR |
Core financing |
|
|
Planning and monitoring of city development strategy (external spatial planners, software, staff) |
45.000 EUR |
Core financing |
-
Closer look at the table of EE services provided by particular partners revealed that almost all partners are developing advanced energy management in their facilities, no matter how large the region is. Another largely implemented EE service by partner regions is support to various applicants in the development of their EE and RES projects acquisition of EE funds available. The scale of services varies from partner to partner, yet, it is possible to conclude that most of the partners regions have advanced support of EE services in their areas:
2.2.2 EE projects
- The table below provides basic overview of EE projects realised in partners areas in recent 5 years upon the classification outlined in the section 1.2 of this document.
Name of the region / area |
EE project(s) |
Amount of funds needed |
Sources of financing |
Emilia – Romagna |
Energy audits for SMEs - realisation of energy audits or adoption of energy management systems |
2.400.000 EUR |
100% public fund (25% National, 75% The Three- Year Implementation Plan 2017-2019 of the new Regional Energy Plan |
|
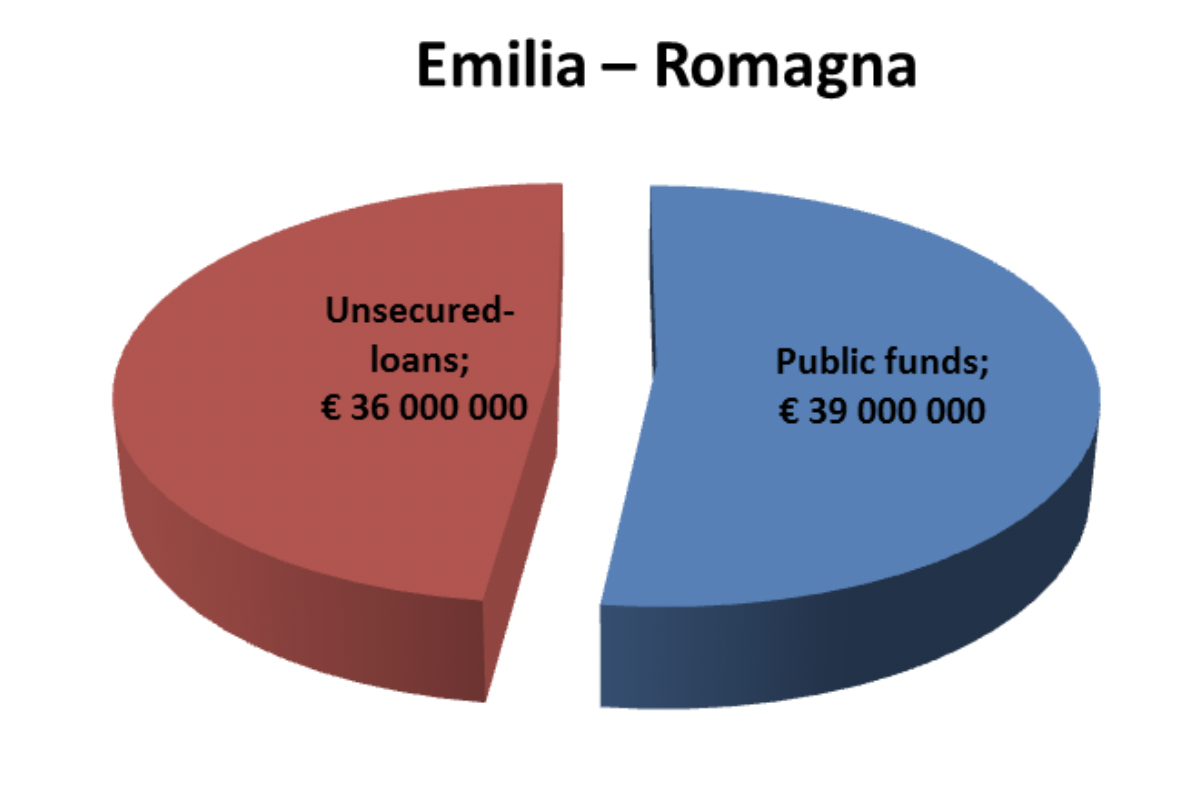
Energy Fund for SMEs - Financial instrument to financial support projects aimed at improving EE and increasing the use of RES |
36.000.000 EUR |
Unsecured-loans at reduced rates with mixed provision resulting partly from the public share (70%) and partly from the private share (30%) for each admissible project |
|
|
Energy efficiency improvement in public buildings and public housing |
36.600.000 EUR |
Fund covering up to the 30% of the total investments for EE interventions |
|
Zlínský kraj |
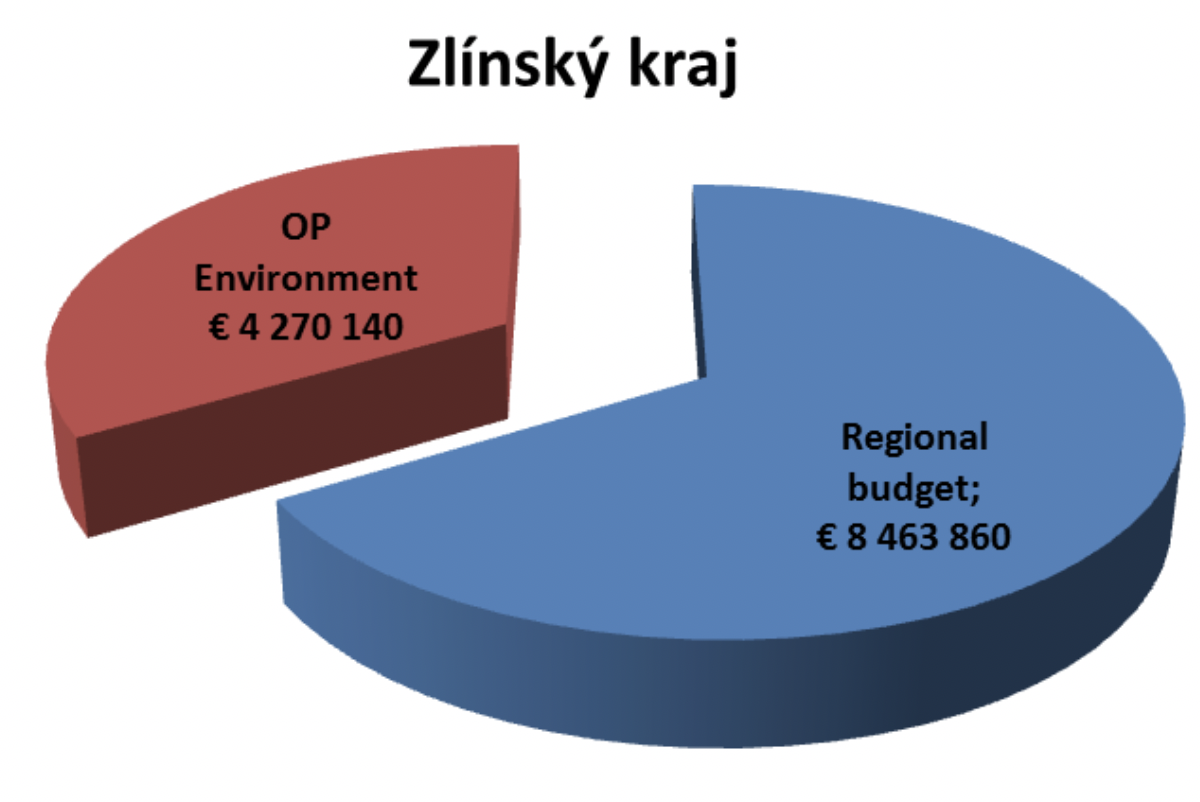
3 investment projects on increasing the energy efficiency in buildings of the Zlín Region (2.615,16 GJ annual energy savings; 145,29 annual CO2 savings) – OP Environment 50th call (I) |
5.099.000 EUR |
Regional budget 58% OP Environment 42% |
|
1 investment project on increasing the energy efficiency in buildings of the Zlín Region (2.371,49 GJ annual energy savings; 125,45 annual CO2 savings) – OP Environment 50th call (II) |
562.000 EUR |
Regional budget 58% OP Environment 42% |
|
|
1 investment project on increasing the energy efficiency in buildings of the Zlín Region (486,50 GJ annual energy savings; 27,03 annual CO2 savings) |
391.000 EUR |
Regional budget 40% OP Environment 60% |
|
|
7 investment projects on increasing the energy efficiency in buildings of the Zlín Region (3.717,6 GJ annual energy savings; 235,11 annual CO2 savings) |
4.536.000 EUR |
Regional budget 72% OP Environment 28% |
|
|
2 investment projects on increasing the energy efficiency in buildings of the Zlín Region (593,3 GJ annual energy savings; 33,28 annual CO2 savings) |
471.000 EUR |
Regional budget 71% OP Environment 29% |
|
|
1 investment project on increasing the energy efficiency in buildings of the Zlín Region (2.202,5 GJ annual energy savings; 147,47 annual CO2 savings) |
1.675.000 EUR |
Regional budget 85% OP Environment 15% |
|
Tolna Megye |
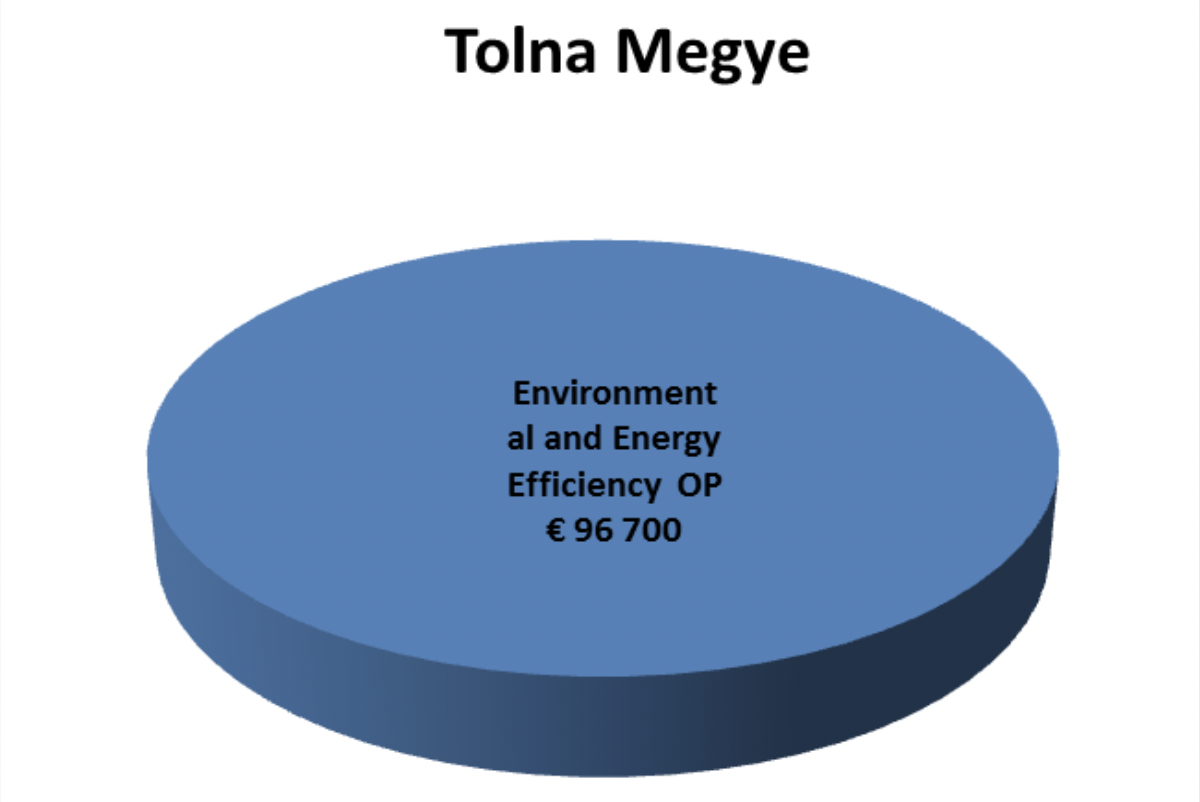
Elaboration of Tolna County’s Climate Strategy leading to the expansion of climate adaptation and climate change prevention of local government leaders, the strengthening of local capacities and the clarity of the Tolna County population. The long-term goal is to apply climate change adaptation and climate change considerations at county level spatial development and town-level urban planning. |
96.700 EUR |
Environmental and Energy Efficiency OP |
Velenje |
Energy renovation of 2 kindergartens - facade renovation, Installation of new windows and roof insulation |
502.765 EUR |
15 % Municipality of Velenje |
|
Energy renovation of healthcare Centre in Velenje - windows , recuperation, new electric and other installations |
1.288.616 EUR |
15 % Municipality of Velenje |
|
|
EnergyrenovationofvilaRožle -windowsandroof insulation |
273.134 EUR |
85% EE Culture |
|
|
Energy renovation of regional gallery of Velenje |
1.381.977 EUR |
70% EU and regional development funds 30% Municipality of Velenje |
|
|
Renovation of business centre Standard |
1.695.975 EUR |
85% EU and regional development funds 15% Municipality of Velenje |
|
Koprivnica |
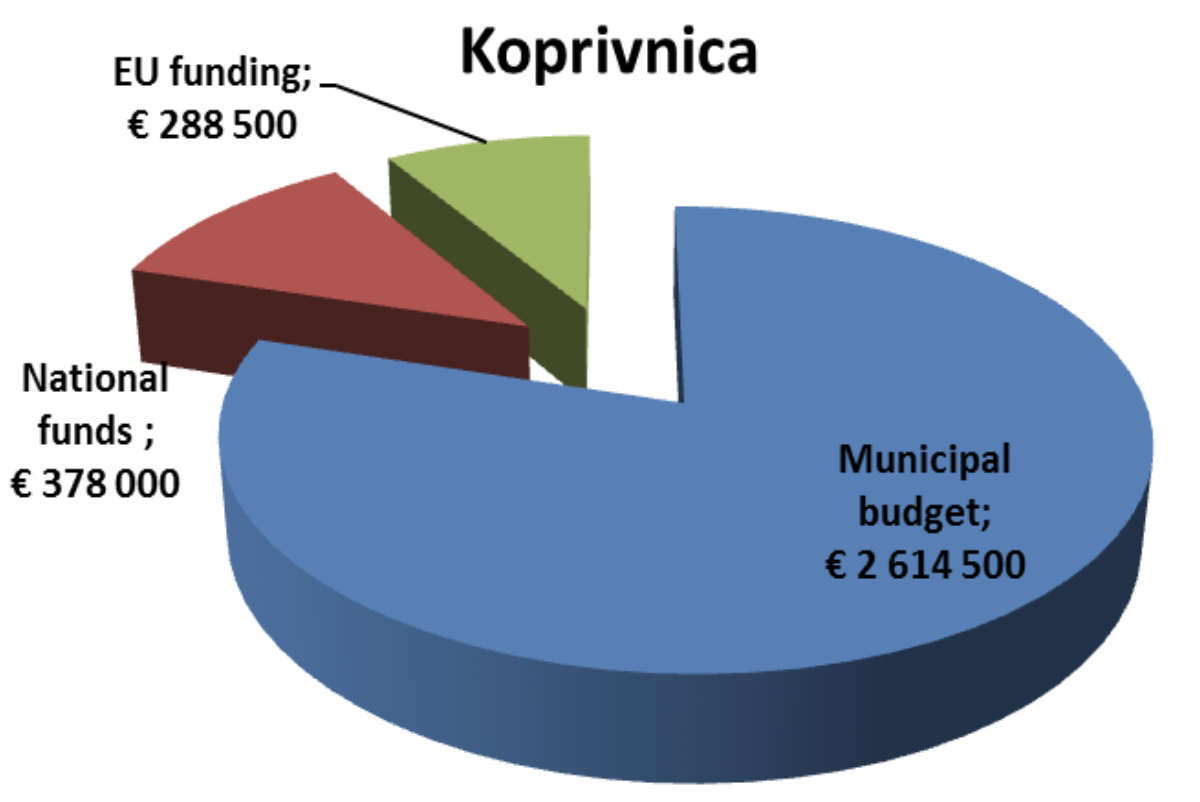
Primary school “A.N. Gostovinski” – lighting system reconstruction |
21.000 EUR |
100% own sources (municipal budget) |
|
Open university Koprivnica, Domoljub odeum hall – New HVAC system |
95.000 EUR |
30% own sources and 70% national ministry |
|
|
Library „Fran Galovic” and movie theatre „Velebit” – heating system |
20.000 EUR |
100% own sources |
|
|
Continuous reconstruction of public lighting in the City of Koprivnica |
130.000,00 |
100% own sources |
|
|
Solar panels for preparation of hot water - kindergarten + institution of education and rehabilitation |
15.000 EUR |
60% own resources 40% national |
|
|
Reconstruction of KC poduzetnik - new façade, new windows, heating separators and PV plant |
230.000 EUR |
15% own sources and 85% national |
|
|
Partial reconstruction of Primary school “Brace Radic” |
100.000 EUR |
100% own sources |
|
|
Partial reconstruction of Community centre “Dom mladih” |
130.000 EUR |
100% own sources |
|
|
nZEB University building |
2.000.000 EUR |
100% own sources |
|
|
Smart metering in public buildings |
10.000 EUR |
15% own sources and 85% EU funding |
|
|
Bike sharing in the City of Koprivnica |
200.000 EUR |
15% own sources and 85% EU funding |
|
|
Electric car pool |
130.000 EUR |
33% own sources 33% national 33% EU funding |
|
|
Electric public transport |
200.000 EUR |
33% own sources 33% national co- financing |
|
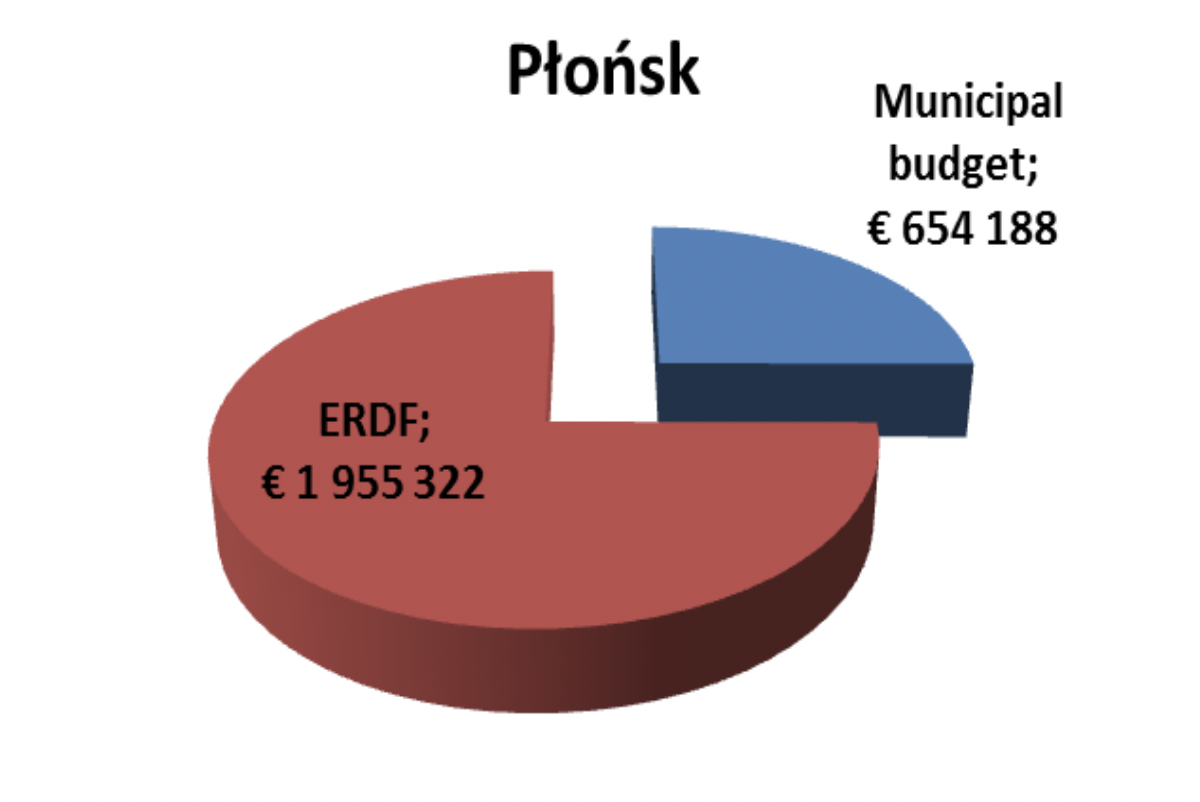
Płońsk |
Insulation of public facilities in Płońsk - Primary School No. 3 and Junior High School No. 1 in Płońsk and the adaptation of the former school in Goszczyce Średnie |
417.202 EUR |
30% Municipal budget |
|
Insulation and purchase and assembly of solar collectors for the Municipal Sports and Recreation Center in Płońsk |
913.636 EUR |
30% |
|
|
Improving the energy efficiency of public buildings in the Commune of the City of Płońsk - deep energy modernization of 4 public buildings |
1.262.721 EUR |
20% |
|
|
Low-Emission Economy Plan for the City of Płońsk |
15.952,38 EUR |
15% |
|
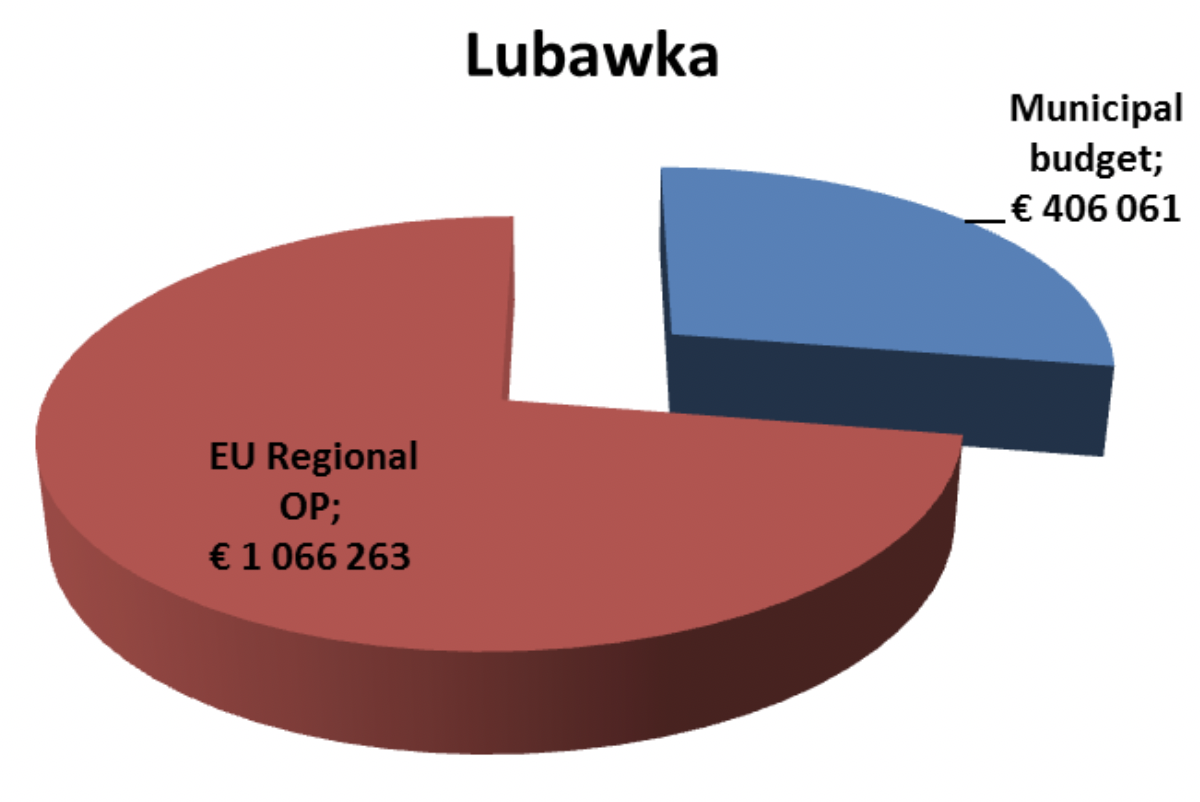
Lubawka |
Reconstruction, thermo-modernization of the Health Center building in Chełmsko Śl. (2013) |
125.000 EUR |
15% municipal budget 85% EU Regional OP |
|
Modernization of sanitary facilities, heating installation and boiler rooms in the Daycare Centre In Bukówka (2013) |
15.000 EUR |
50% municipal budget 50% EU Regional OP |
|
|
Modernization with the enlargement of the Public Schools Complex at. Mickiewicza St. 4 in Lubawka, stages V and VI (2014) |
161.300 EUR |
municipal budget |
|
|
Purchase and installation of a steam boiler in the Public Schools Complex in Chełmsko Śląskie (2015) |
2.890 EUR |
municipal budget |
|
|
Reconstruction, thermo-modernization of the primary school building in Miszkowice (2014-15) |
139.300 EUR |
25% municipal budget 75% EU Regional OP |
|
|
Increasing the energy efficiency of the building of the Public Schools Complex in Chełmsko Śląskie (2017) |
708.250 EUR |
18% municipal budget 82% EU Regional OP |
|
|
Improving conditions of primary and secondary education through building enlargement and reconstruction of the Public School Complex in Lubawka, 1st stage (2017-18) – heating system + hot water system |
104.470 EUR |
20% municipal budget 80% EU Regional OP |
|
|
Increasing energy efficiency of the historic City Hall building in Lubawka (2017-18) |
216.115 EUR |
15% municipal budget 85% EU Regional OP |
|
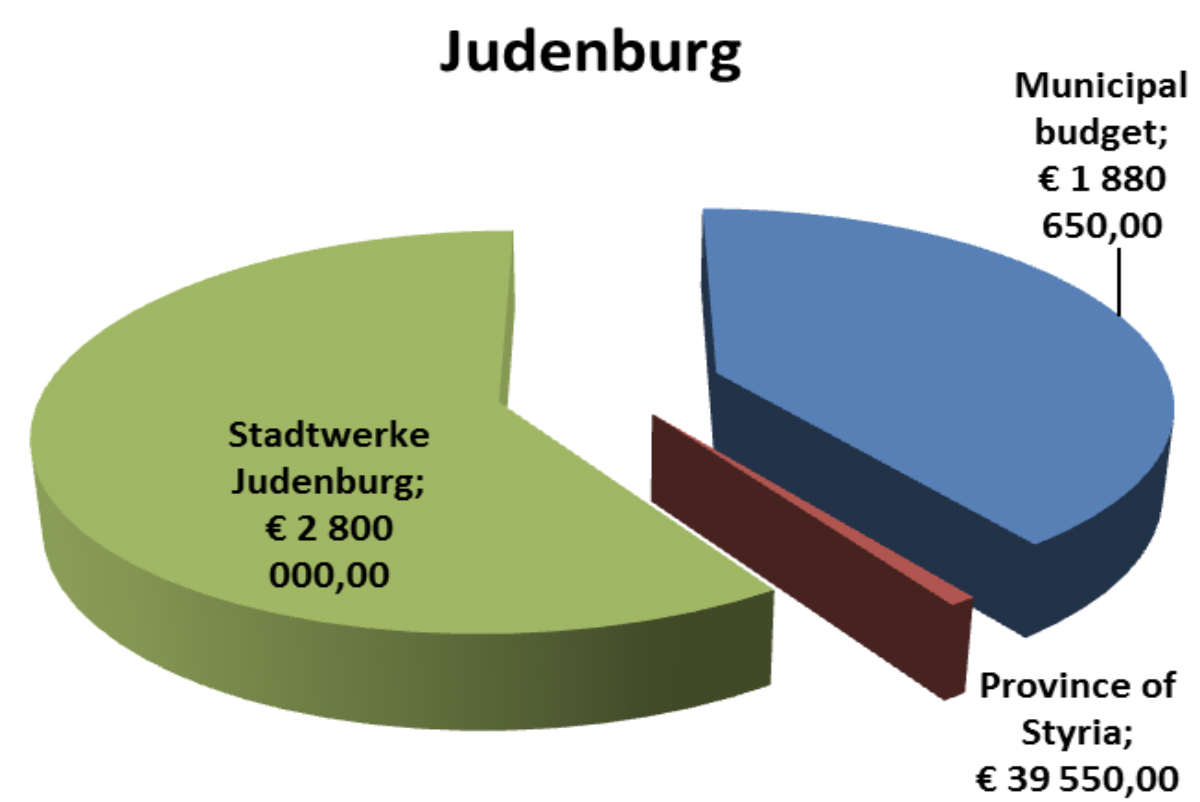
Judenburg |
Conversion of public lighting to LED technology - public lighting is gradually replaced with LED from 2016 to 2024. Figure is for 2016 – 2018. |
230.000 EUR |
100 % |
|
Conversion of Christmas lighting to LED - 40 year old lightbulb Christmas lighting in inner city for new LED technology |
220.000 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Renovation of kindergartens Spielgasse, Strettweg, Jägersteig - windows, new lighting, e-installation |
56.500 EUR |
30% municipal budget 70% Province of Styria |
|
|
Renovations in kindergartens without funding |
9.400 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Primary school City and special needs school |
26.400 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Town hall: roof renovation |
7.000 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Primary school Lindfeld - Renovation of WCs, roof, lighting and heating system |
66.500 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Comprehensive and polytechnical school - Renovation of WCs, lighting and heating system, partial thermal insulation |
65.000 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Venue centre - Renovation of lighting, ventilation and heating system, partial thermal insulation and roof renovation |
35.000 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Sports hall Lindfeld - Renovation of WCs and heating system |
4.400 EUR |
100 % |
|
|
Construction of a district heating grid (The 70% investment is from the Stadtwerke Judenburg, which is an ESCO, 100 % owned by the city) |
4.000.000 EUR |
30% municipal budget, 70 % Stadtwerke |
Putting information and figures into graphical form we get an interesting overview of sources of financing of EE projects partners regions have relied on in last 5 years:
While regions are mostly relying on own budgets, or in the case of Tolna County on funding from existing operational programmes, the municipalities has slightly more variable portfolio in EE projects financing.
In the case of Emilia-Romagna region an advanced way of EE financing supported by the region is used. They are so called “unsecured loans” which are closely described in the chapter 2.5 of this document - Best Practice Factsheet #2 - Emilia-Romagna, Italy, Energy Fund - Multyscope Regional Fund of public financing.
Municipalities, with the exception of Judenburg, are relying to some extent to existing sources from EU funds which is the logical way of EE project financing when such funds are available. However, to lower the dependence on this way of financing and decrease the threat of not achieving these grants in the future it would be advisable to consider more diverse ways of EE financing in newly developed strategies and financial roadmaps.
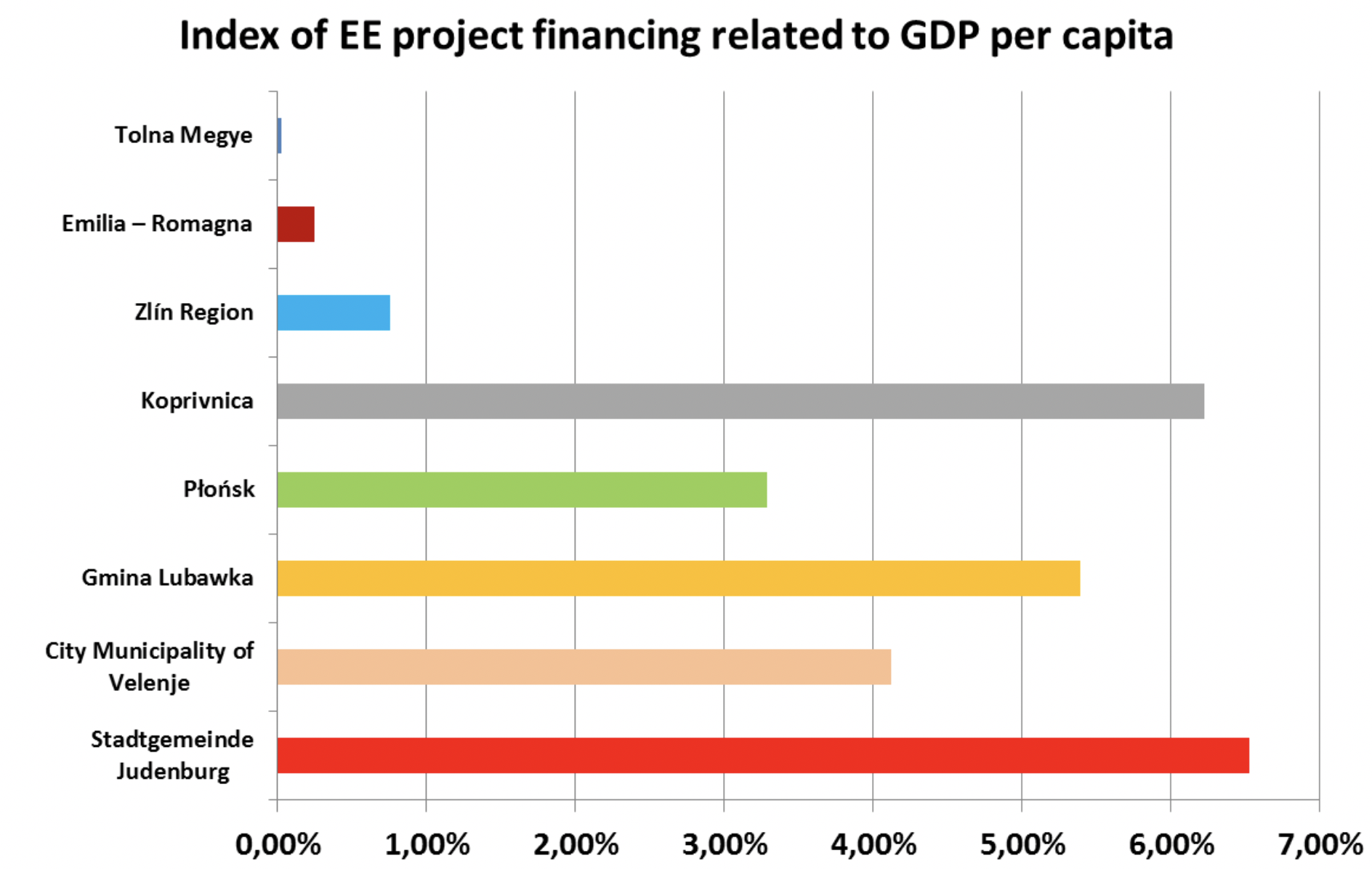
Overview of EE project financing in partners ́regions
Name of the region / area |
(1) GDP per capita (2016) |
(2) Amount of project EE financing |
(3) Amount of project EE financing per capita |
(4) Index of EE project financing to GDP per capita |
Emilia – Romagna |
€ 34 752 |
€ 75 000 000,00 |
€ 84,62 |
0,24% |
Zlín Region |
€ 14 479 |
€ 12 734 000,00 |
€ 109,02 |
0,75% |
Tolna Megye |
€ 8 566 |
€ 96 700,00 |
€ 2,18 |
0,03% |
City Municipality of Velenje |
€ 18 050 |
€ 5 142 467,00 |
€ 743,20 |
4,12% |
Płońsk |
€ 17 646 |
€ 2 609 511,38 |
€ 579,89 |
3,29% |
Stadtgemeinde Judenburg |
€ 35 948 |
€ 4 720 200,00 |
€ 2 345,32 |
6,52% |
Koprivnica |
€ 8 548 |
€ 3 281 000,00 |
€ 531,70 |
6,22% |
Gmina Lubawka |
€ 12 294 |
€ 1 472 325,00 |
€ 662,67 |
5,39% |
We can see a difference between regions and municipalities again. Municipalities are in general investing more in EE projects in relation to the population living in the area but we can see regions are investing to its own property some considerable amounts of money as well. Just with the exception of Tolna County as counties in Hungary only possess a few objects like cultural buildings or museums.
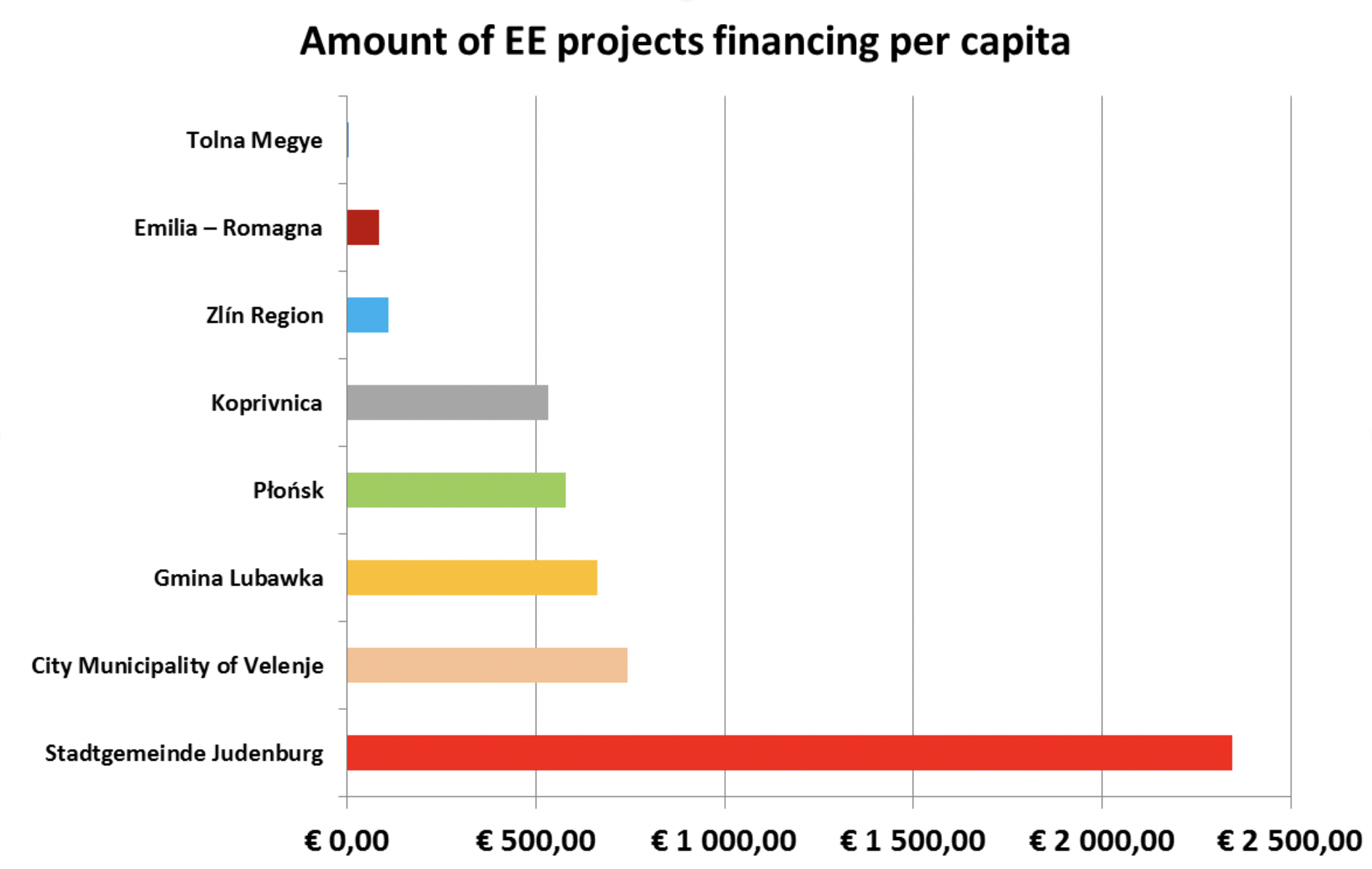
If we list the areas by the “Amount of project financing per capita”, we will get the following comparison:
Such a result reflects, more or less, the economic power of particular regions. However, we will get an interesting comparison of EE projects financing in partners ́ regions when the economic power of each region is equalized with the help of the “Index of EE project financing related to GDP per capita” = column 3 / column 1 of the table above.
This graph reveals that municipalities relying more on its own municipal budgets (Koprivnica, Lubawka) are investing relatively more in EE projects than municipalities trying to maximize external EU funds (Velenje, Płońsk). This conclusion is not possible to generalize, yet, within compared areas it is valid. Judenburg still comes out from this indexation as the most EE investing area, however, its position is not so dominant as it seems without equalizing the economic power.